The letter N stands for nitrogen. Though it can't be directly used by humans from the air or soil, it is abundant in the environment. Microbes and green plants are what they rely on to transform it into a form that can be used. However, the question of why and how humans use nitrogen remains. Your body needs nitrogen to produce the proteins found in your DNA, muscles, skin, blood, hair, and nails. The Royal Society of Chemistry states that diets high in protein provide you with nitrogen. Meat, seafood, beans, nuts, eggs, milk, and other dairy products are some examples of these foods.
How It Works
Virtual Chembook at Elmhurst College says your body needs nitrogen from protein-rich diets to create human proteins. Enzymes, which are needed for metabolism, and tissues contain proteins. RNA and DNA, which make up your genes, contain nitrogen.
Features
Normal growth, tissue repair, and cell regeneration require nitrogen. Nitrogen is abundant in the environment, but people need microbes and green plants to use it. Your body recycles nitrogen from amino acids.
If not required for protein formation, the amino acids may be broken down into nitrogen for energy. Nitrogen can also be used to make non-protein molecules like hemoglobin's heme, which moves oxygen in red blood cells.
Requirements
About 105 milligrams of nitrogen per kilogram, or 2.2 pounds, per day are required for a healthy adult male. The International Dairy Federation states that 0.83-0.83 grams of protein per kilogram per day is adequate to meet daily needs for nitrogen. In order to meet his daily demands for nitrogen, a 220-pound guy would require 83 grams, or around 3 ounces, of protein. Ammonia is a nitrogen-containing waste product that your body gets rid of when proteins break down.
Additional Information
Ammonia is removed from your body by your body converting it to urea, which is subsequently excreted in urine by your kidneys. Nitrogen is thus released back into the environment. Americans, in contrast to populations in developing nations, rarely suffer from a deficiency of dietary nitrogen unless they follow very strict diets deficient in protein. Symptoms of deficiency include brittle hair wasting, delayed wound healing, muscle weakness, and hair loss.
Is Nitrogen Important For The Human Body?
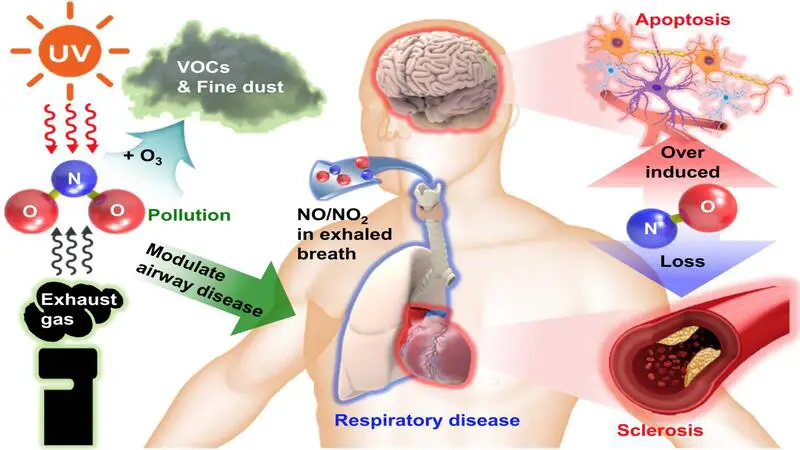
Animals and plants require survival. It is among the fundamental elements of existence. 80% of our atmosphere is composed of it. Our bodies need it to produce proteins and amino acids. Nucleic acids, which are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, also require it. Nitrogen in a 'fixed' reactive form is necessary for humans and other earthly animals. What is the purpose of reactive nitrogen, do you know?
It is essential to the process of producing food. We could prepare food like manure with naturally available nitrogen up until 1900. Reactive nitrogen, however, can now be fixed thanks to the development of an industrial method called the Haber-Bosch process, which aids in the processing of food.
How Do We Intake Nitrogen In Our Body?
We know that a significant portion of the Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen. Although nitrogen cannot be used by humans through respiration, it can be absorbed by eating plants or animals that have eaten vegetation high in nitrogen. Since over 78% of the air we breathe contains nitrogen, it constantly enters our bodies. Protein synthesis is aided by nitrogen, and amino acids affect immunological function, development, hormones, and the brain.
Why Does Our Body Need Nitrogen?

Humans require amino acids, as was previously said, and nitrogen is a key component that aids in the synthesis of human proteins. Enzymes, which are made up of several types of proteins, are essential to our body's metabolic processes. Your genes are made up of the nucleic acid DNA, and RNA is involved in the nitrogen-dependent process of protein synthesis. We are all aware that life would not exist without DNA. The human body needs nitrogen for growth and healthy food digestion. It plays a crucial role in the human fetus's development. Nitrogen is necessary for the synthesis of new cells in tissue repair and cell replacement.
Conclusion
Because it is involved in the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other compounds vital to the growth, development, and metabolism of the human body, nitrogen is an element required for human life. Humans get their nitrogen from the food they eat, especially protein-rich meals, and nitrogen is eventually recycled through a number of metabolic pathways.